GWT Composite
GWTのWidgetはHTMLのDOM要素に対応したクラスが用意されているが、他のGUIツールキットのようにそれらを組み合わせて大きな一つのGUIコンポーネントを作ることができる。それには複数の方法があるのだが、そのひとつはCompositeクラスを利用することだ。
Composite(com.google.gwt.user.client.ui.Composite)クラスはその名の通り、複数のウィジェットクラスから構成された一つの大きなウィジェットとして、また、他のウィジェットを配置するコンテナとして振舞うクラスである。
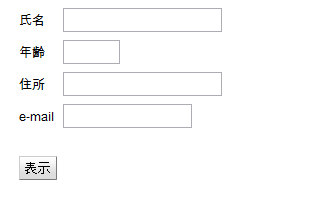
AddressInfoForm
Composite具象クラスの例として住所録データを入力するために4つのラベルとテキストボックス、1つのボタンを格子状に配置したAdddressInfoFormクラスを定義する。
public class AddressInfoForm extends Composite {
private Grid grid = new Grid(6,2);
private Label fullNameLabel = new Label("氏名");
private TextBox fullNameTextBox = new TextBox();
private Label ageLabel = new Label("年齢");
private TextBox ageTextBox = new TextBox();
private Label addressLabel = new Label("住所");
private TextBox addressTextBox = new TextBox();
private Label emailLabel = new Label("e-mail");
private TextBox emailTextBox = new TextBox();
private Button button = new Button();
private AddressInfo addressInfo;
public AddressInfoForm(String buttonText, ClickHandler buttonClickHandler) {
initWidget(grid);
button.setText(buttonText);
grid.addStyleName("addressGrid");
addressTextBox.setVisibleLength(20);
emailTextBox.setVisibleLength(15);
ageTextBox.setVisibleLength(3);
grid.setWidget(0, 0, fullNameLabel); grid.setWidget(0, 1, fullNameTextBox);
grid.setWidget(1, 0, ageLabel); grid.setWidget(1, 1, ageTextBox);
grid.setWidget(2, 0, addressLabel); grid.setWidget(2, 1, addressTextBox);
grid.setWidget(3, 0, emailLabel); grid.setWidget(3, 1, emailTextBox);
grid.setWidget(5, 0, button);
button.addClickHandler(buttonClickHandler);
}
void assign(AddressInfo addressInfo) {
this.addressInfo = addressInfo;
fullNameTextBox.setText(addressInfo.fullName);
ageTextBox.setText(String.valueOf(addressInfo.age));
addressTextBox.setText(addressInfo.address);
emailTextBox.setText(addressInfo.email);
}
public AddressInfo getAddressInfo() {
return this.addressInfo;
}
public Button getButton() {
return button;
}
}
Gridクラスは各ウィジェットを格子状に配置するためのマトリクスとして使用している。
このように定義したCompositeクラスの派生クラスは、EntryPointから簡単に利用できる。
AddressInfoFormを利用する (AddressBookクラス)
public class AddressBook implements EntryPoint {
final private AddressInfoForm form = new AddressInfoForm("表示", new ShowPlaceHandler());
private final GreetingServiceAsync greetingService = GWT.create(GreetingService.class);
public void onModuleLoad() {
RootPanel.get("addressInfoContainer").add(form);
}
private class ShowPlaceHandler implements ClickHandler {
public void onClick(ClickEvent event) {
//ボタンが押下された際の処理
}
}
}
AddressBook.html
<html>
<head>
<meta http-equiv="content-type" content="text/html; charset=UTF-8">
<link type="text/css" rel="stylesheet" href="AddressBook.css">
<script type="text/javascript" language="javascript" src="testecho/testecho.nocache.js"></script>
</head>
<body>
<table align="center">
<tr>
<td id="addressInfoContainer"></td>
</tr>
</table>
</body>
</html>実行時にはid="addressInfoContainer"で識別されたtd要素にRootpanelがバインドされて、その後AddressInfoForm が挿入〜表示される。